Setting Up the ADT Bundle
The ADT Bundle provides everything you need to start developing apps, including a version of the Eclipse IDE with built-inADT (Android Developer Tools) to streamline your Android app development. If you haven't already, go download theAndroid ADT Bundle. (If you downloaded the SDK Tools only, for use with an existing IDE, you should instead read Setting Up an Existing IDE.)
Install the SDK and Eclipse IDE
- Unpack the ZIP file (named
adt-bundle-<os_platform>.zip) and save it to an appropriate location, such as a "Development" directory in your home directory. - Open the
adt-bundle-<os_platform>/eclipse/directory and launch eclipse.
That's it! The IDE is already loaded with the Android Developer Tools plugin and the SDK is ready to go. To start developing, read Building Your First App.
Caution: Do not move any of the files or directories from the
adt-bundle-<os_platform> directory. If you move theeclipse or sdk directory, ADT will not be able to locate the SDK and you'll need to manually update the ADT preferences.Additional information
As you continue developing apps, you may need to install additional versions of Android for the emulator and other packages such as the library for Google Play In-app Billing. To install more packages, use the SDK Manager.
Everything you need to develop Android apps is on this web site, including design guidelines, developer training, API reference, and information about how you can distribute your app. For additional resources about developing and distributing your app, see the Developer Support Resources.
Getting started on Windows
Your download package is an executable file that starts an installer. The installer checks your machine for required tools, such as the proper Java SE Development Kit (JDK) and installs it if necessary. The installer then saves the Android SDK Tools into a default location (or you can specify the location).
- Double-click the executable (
.exefile) to start the install. - Make a note of the name and location in which it saves the SDK on your system—you will need to refer to the SDK directory later, when setting up the ADT plugin and when using the SDK tools from the command line.
- Once the installation completes, the installer offers to start the Android SDK Manager. If you'll be using Eclipse, do notstart the Android SDK Manager, and instead move on to Installing the Eclipse Plugin.If you're using a different IDE, start the SDK Manager and read Adding Platforms and Packages.
Installing the Eclipse Plugin
Android offers a custom plugin for the Eclipse IDE, called Android Development Tools (ADT). This plugin provides a powerful, integrated environment in which to develop Android apps. It extends the capabilities of Eclipse to let you quickly set up new Android projects, build an app UI, debug your app, and export signed (or unsigned) app packages (APKs) for distribution.If you need to install Eclipse, you can download it from eclipse.org/mobile.Note: If you prefer to work in a different IDE, you do not need to install Eclipse or ADT. Instead, you can directly use the SDK tools to build and debug your application.Download the ADT Plugin
- Start Eclipse, then select Help > Install New Software.
- Click Add, in the top-right corner.
- In the Add Repository dialog that appears, enter "ADT Plugin" for the Name and the following URL for the Location:
https://dl-ssl.google.com/android/eclipse/
- Click OK.If you have trouble acquiring the plugin, try using "http" in the Location URL, instead of "https" (https is preferred for security reasons).
- In the Available Software dialog, select the checkbox next to Developer Tools and click Next.
- In the next window, you'll see a list of the tools to be downloaded. Click Next.
- Read and accept the license agreements, then click Finish.If you get a security warning saying that the authenticity or validity of the software can't be established, click OK.
- When the installation completes, restart Eclipse.
Configure the ADT Plugin
Once Eclipse restarts, you must specify the location of your Android SDK directory:- In the "Welcome to Android Development" window that appears, select Use existing SDKs.
- Browse and select the location of the Android SDK directory you recently downloaded and unpacked.
- Click Next.
Your Eclipse IDE is now set up to develop Android apps, but you need to add the latest SDK platform tools and an Android platform to your environment. To get these packages for your SDK, continue to Adding Platforms and Packages.Troubleshooting Installation
If you are having trouble downloading the ADT plugin after following the steps above, here are some suggestions:- If Eclipse can not find the remote update site containing the ADT plugin, try changing the remote site URL to use http, rather than https. That is, set the Location for the remote site to:
http://dl-ssl.google.com/android/eclipse/
- If you are behind a firewall (such as a corporate firewall), make sure that you have properly configured your proxy settings in Eclipse. In Eclipse, you can configure proxy information from the main Eclipse menu in Window (on Mac OS X, Eclipse) > Preferences > General > Network Connections.
If you are still unable to use Eclipse to download the ADT plugin as a remote update site, you can download the ADT zip file to your local machine and manually install it:- Download the ADT Plugin zip file (do not unpack it):
Package Size MD5 Checksum ADT-21.0.1.zip 13569302 bytes acfb01bf3fd1240f1fc21488c3dd16bf - Start Eclipse, then select Help > Install New Software.
- Click Add, in the top-right corner.
- In the Add Repository dialog, click Archive.
- Select the downloaded ADT-21.0.1.zip file and click OK.
- Enter "ADT Plugin" for the name and click OK.
- In the Available Software dialog, select the checkbox next to Developer Tools and click Next.
- In the next window, you'll see a list of the tools to be downloaded. Click Next.
- Read and accept the license agreements, then click Finish.If you get a security warning saying that the authenticity or validity of the software can't be established, click OK.
- When the installation completes, restart Eclipse.
To update your plugin once you've installed using the zip file, you will have to follow these steps again instead of the default update instructions.Adding Platforms and Packages
The Android SDK separates tools, platforms, and other components into packages you can download using the Android SDK Manager. The original SDK package you've downloaded includes only the SDK Tools. To develop an Android app, you also need to download at least one Android platform and the latest SDK Platform-tools.- Launch the SDK Manager.If you've used the Windows installer to install the SDK tools, you should already have the Android SDK Manager open. Otherwise, you can launch the Android SDK Manager in one of the following ways:
- On Windows, double-click the
SDK Manager.exefile at the root of the Android SDK directory. - On Mac or Linux, open a terminal and navigate to the
tools/directory in the Android SDK, then executeandroid sdk.
- On Windows, double-click the
- The SDK Manager shows all the SDK packages available for you to add to your Android SDK. As a minimum configuration for your SDK, we recommend you install the following:
- The latest Tools packages (check the Tools folder).
- The latest version of Android (check the first Android folder).
- The Android Support Library (open the Extras folder and check Android Support Library).
Once you've chosen your packages, click Install. The Android SDK Manager installs the selected packages into your Android SDK environment.
With these packages installed, you're ready to start developing. To get started, read Building Your First App.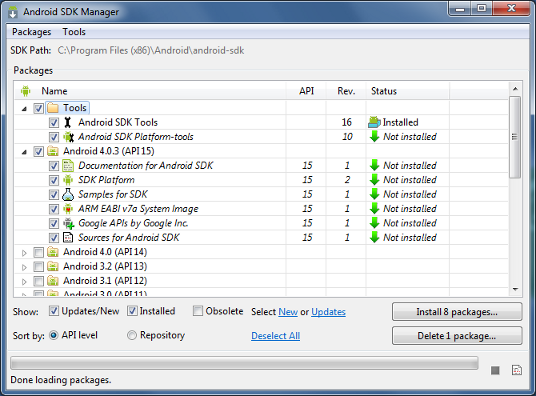 Figure 1. The Android SDK Manager shows the SDK packages that are available, already installed, or for which an update is available.The Android SDK is composed of modular packages that you can download separately using the Android SDK Manager. For example, when the SDK Tools are updated or a new version of the Android platform is released, you can use the SDK Manager to quickly download them to your environment. Simply follow the procedures described in Adding Platforms and Packages.There are several different packages available for the Android SDK. The table below describes most of the available packages and where they're located once you download them.
Figure 1. The Android SDK Manager shows the SDK packages that are available, already installed, or for which an update is available.The Android SDK is composed of modular packages that you can download separately using the Android SDK Manager. For example, when the SDK Tools are updated or a new version of the Android platform is released, you can use the SDK Manager to quickly download them to your environment. Simply follow the procedures described in Adding Platforms and Packages.There are several different packages available for the Android SDK. The table below describes most of the available packages and where they're located once you download them.Available Packages
Package Description File Location SDK Tools Contains tools for debugging and testing, plus other utilities that are required to develop an app. If you've just installed the SDK starter package, then you already have the latest version of this package. Make sure you keep this up to date. <sdk>/tools/SDK Platform-tools Contains platform-dependent tools for developing and debugging your application. These tools support the latest features of the Android platform and are typically updated only when a new platform becomes available. These tools are always backward compatible with older platforms, but you must be sure that you have the latest version of these tools when you install a new SDK platform. <sdk>/platform-tools/Documentation An offline copy of the latest documentation for the Android platform APIs. <sdk>/docs/SDK Platform There's one SDK Platform available for each version of Android. It includes an android.jarfile with a fully compliant Android library. In order to build an Android app, you must specify an SDK platform as your build target.<sdk>/platforms/<android-version>/System Images Each platform version offers one or more different system images (such as for ARM and x86). The Android emulator requires a system image to operate. You should always test your app on the latest version of Android and using the emulator with the latest system image is a good way to do so. <sdk>/platforms/<android-version>/Sources for Android SDK A copy of the Android platform source code that's useful for stepping through the code while debugging your app. <sdk>/sources/Samples for SDK A collection of sample apps that demonstrate a variety of the platform APIs. These are a great resource to browse Android app code. The API Demos app in particular provides a huge number of small demos you should explore. <sdk>/platforms/<android-version>/samples/Google APIs An SDK add-on that provides both a platform you can use to develop an app using special Google APIs and a system image for the emulator so you can test your app using the Google APIs. <sdk>/add-ons/Android Support A static library you can include in your app sources in order to use powerful APIs that aren't available in the standard platform. For example, the support library contains versions of the Fragmentclass that's compatible with Android 1.6 and higher (the class was originally introduced in Android 3.0) and theViewPagerAPIs that allow you to easily build a side-swipeable UI.<sdk>/extras/android/support/Google Play Billing Provides the static libraries and samples that allow you to integrate billing services in your app with Google Play. <sdk>/extras/google/Google Play Licensing Provides the static libraries and samples that allow you to perform license verification for your app when distributing with Google Play. <sdk>/extras/google/The above table is not comprehensive and you can add new sites to download additional packages from third-parties.In some cases, an SDK package may require a specific minimum revision of another package or SDK tool. For example, there may be a dependency between the ADT Plugin for Eclipse and the SDK Tools package. When you install the SDK Tools package, you should also upgrade to the required version of ADT (if you are developing in Eclipse). In this case, the major version number for your ADT plugin should always match the revision number of your SDK Tools (for example, ADT 8.x requires SDK Tools r8).The development tools will notify you with debug warnings if there is dependency that you need to address. The Android SDK Manager also enforces dependencies by requiring that you download any packages that are needed by those you have selected.Adding New Sites
By default, Available Packages displays packages available from the Android Repository and Third party Add-ons. You can add other sites that host their own Android SDK add-ons, then download the SDK add-ons from those sites.For example, a mobile carrier or device manufacturer might offer additional API libraries that are supported by their own Android-powered devices. In order to develop using their libraries, you must install their Android SDK add-on, if it's not already available under Third party Add-ons.If a carrier or device manufacturer has hosted an SDK add-on repository file on their web site, follow these steps to add their site to the Android SDK Manager:- Select Available Packages in the left panel.
- Click Add Add-on Site and enter the URL of the
repository.xmlfile. Click OK.
Any SDK packages available from the site will now be listed under a new item named User Add-ons.Samples
To help you understand some fundamental Android APIs and coding practices, a variety of sample code is available from the Android SDK Manager. Each version of the Android platform available from the SDK Manager offers its own set of sample apps.To download the samples:- Launch the Android SDK Manager.
- On Windows, double-click the SDK Manager.exe file at the root of the Android SDK directory.
- On Mac or Linux, open a terminal to the
tools/directory in the Android SDK, then executeandroid sdk.
- Expand the list of packages for the latest Android platform.
- Select and download Samples for SDK.
When the download is complete, you can find the source code for all samples at this location:<sdk>/samples/android-<version>/The<version>number corresponds to the platform's API level.You can easily create new Android projects with the downloaded samples, modify them if you'd like, and then run them on an emulator or device